How to Kill All Bacteria When Roasting Beef

Food Safe Focus (130th Event, May 2017 ) – Nutrient Safety Platform
Bacteria in Raw Meat vs Cooked Meat
Reported by Dr. Fiona FONG, Enquiry Officer,
Hazard Cess Section,
Heart for Nutrient Safety
Recently, bacterial contamination of meat has attracted public attending. Co-ordinate to the World Health Organization, contagion of nutrient past microbiological agents is a worldwide public health business; and most countries have documented meaning increases over the past few decades in the incidence of diseases caused past microorganisms in food. In this article, we will introduce some factors that make up one's mind the growth of bacteria in food, and discuss the unlike food safety considerations for leaner in raw meat and cooked meat and the measures to reduce risks of food poisoning caused past bacteria.
Factors Determining the Growth of Bacteria in Food
Leaner grow best when intrinsic and extrinsic properties are optimal for their growth. Intrinsic properties are the properties that are inherent parts of the nutrient, such equally pH and h2o activity, while extrinsic properties are the backdrop of the environment in which the food is stored, such as temperature. H2o action is not the aforementioned as the wet content of the food simply is a measure out, ranging from 0 to one, of the availability of water in food which determines the growth and survival of leaner. Past controlling these factors (due east.grand. controlling the storage temperature of the food), bacterial overgrowth tin can be prevented.
Bacteria in Raw Meat
Fresh meat is a highly nutritious substrate with h2o activity of about 0.99, meaning that it is suitable for the growth of well-nigh microorganisms. Raw meat in general contains bacteria, including pathogenic and spoilage ones. Every bit warm-blooded animals naturally bear bacteria such equally Salmonella spp. in their intestines, raw meat may be contaminated with bacteria during the slaughtering process such as evisceration and dressing procedures. In addition, the equipment and tools used in the processes, the hands and wear of personnel likewise equally the environment may besides contaminate the meat with bacteria.
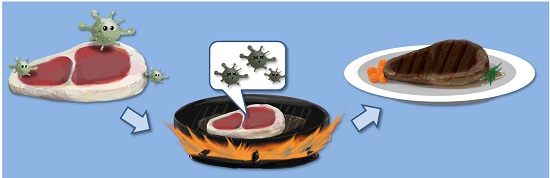
Raw meat should be cooked thoroughly earlier consumption.
Meat has potential to deport foodborne pathogens that can cause illness and lead to food safety problems. These pathogenic bacteria are able to invade our bodies or produce toxins to cause disease. They cannot be seen or smelled on the meat, but can generally be killed past normal cooking conditions (i.due east. cooking to a core temperature of at least 75°C instantaneously or other effective time/ temperature combinations).
Pathogenic bacteria may need to compete with other bacterial flora (e.m. spoilage bacteria) for growth on the meat. Certain pathogenic bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus are relatively poor competitors and may be outgrown by other flora. Spoilage bacteria will cause food to deteriorate or lose quality by developing a bad odour or feeling mucilaginous on the outside of the meat, signs that consumers would unremarkably observe. These spoilage bacteria are unremarkably not harmful, however, when consumed in very large numbers, they can cause gastrointestinal disturbance. Consumers should throw abroad the meat that shows any signs of food spoilage.
Bacteria in Cooked Meat
Every bit mentioned above, thorough cooking tin can generally destroy about bacteria on raw meat, including pathogenic ones. Nevertheless, if there are subsequent lapses in nutrient condom practices, food poisoning may still occur. To start with, raw meat may be contaminated with spores of sure pathogenic bacteria (due east.g. Clostridium perfringens) and spores are not readily destroyed by normal cooking temperature. Estrus of cooking can rather activate the spores to germinate and develop into vegetative cells which can multiply rapidly in foods that are placed at ambient temperature for a long period. Consuming foods that contain loftier levels of Clostridium perfringens vegetative cells may lead to foodborne affliction.
In addition, pathogenic leaner may be introduced into the ready-to-consume cooked meat through cross-contagion and multiply to larger amount equally a result of time and temperature abuse of the food, causing foodborne illness in consumers.
Measures to Reduce Risks of Nutrient Poisoning Caused by Leaner
To prevent food poisoning, raw meat should exist cooked thoroughly before consumption. The set up-to-eat cooked meat should be discarded if it has been held at room temperature for more than 4 hours. If the cooked meat is held at room temperature for less than two hours, information technology tin be refrigerated for final use later or used before the iv hours limit is upwards.
Moreover, good hygienic practices should exist observed. Hands, cutting boards, knives, and other utensils should be washed thoroughly afterward touching raw meat. Measures should be adopted to the prevention of cross contagion between raw meat and ready-to-eat foods including cooked meat, e.g. using i cut lath for ready-to-eat foods and a separate one for raw meat.
Source: https://www.cfs.gov.hk/english/multimedia/multimedia_pub/multimedia_pub_fsf_130_02.html
0 Response to "How to Kill All Bacteria When Roasting Beef"
Publicar un comentario